本文介绍一种工作的所有功能于一身的自动无线电攻击,没有任何互联网连接或其它外部连接或影响执行上的客户端类型的MITM攻击。
在外行人而言; 这种便携式电池供电设备能够自动吸引的无线设备连接到它,是因为iPhone手机/ ipad公司,机器人和其他手机或笔记本电脑和个人电脑。大多数设备将自动连接到它无需用户甚至没有意识到。该设备将提供一个假的网络中运行的假电子邮件和Web服务器,并使用一些网络挂羊头卖狗肉,将捕获任何试图连接的主机名,用户名和密码,并记录它,随着GPS坐标,其中的细节被抓获的。该设备可用于劫持的企业和个人电子邮件登录、Facebook的登录、等等。
在摆弄airbase-ng aircrack-ng套件的一部分,在过去的几个月,研究无线客户端漏洞导致一个有趣的概念验证项目。有一些缺点在当前广泛使用的无线技术。然而,第一个项目的一个解释。项目描述是发射无线中间人这个攻击,而无需另一个终端连接的受害者。我们需要创建一个MITM攻击没有任何互联网接入。这样的攻击理论上可以用于管,在锁定建筑,此举,等等,没有移动数据卡的使用。之上的修改覆盆子中欧地区,尽管任何Linux发行版将是合适的,我已经把我的无线设备30 dbm的输出功率,并开始自动化流程如下:
首先,一个空军基地实例在我rtl8187卡如下;
/usr/local/sbin/airbase-ng -c 3 wlan0 –essids “/root/pen/code/scripts/essids” -P -C 60 -I 60 -vv|grep –line-buffered “directed probe request”| tee /run/probes
这开始一个接入点3频道,指引中包含的ssid /root/pen/code/scripts/essids以及任何调查请求访问点可能收到客户希望连接到访问点。现在,在更多的细节,定期“non-hidden”接入点将播出“灯塔”指定的数据块的SSID(无线网络名称)以及支持加密类型等等。这些信号通常发送的每100毫秒。无线客户端将发送探测包,包含所有无线网络的ssid,存储,并要求如果他们都在这里。
Fully Automatic Wireless Hacking Station
April 26, 2013/14 Comments/in Linux, Perl, Projects, Raspberry Pi, Security Consultant, Wireless /by Adam Palmer+
This article describes a working all-in-one standalone mobile wireless attack station that can perform MITM type attacks on clients automatically and without any internet access or other external connectivity or influence.
In laypersons terms; this portable battery powered device can automatically entice wireless devices to connect to it, be that iPhones/iPads, Androids and other phones or laptops and PCs. Most devices will connect to it automatically without the user even realizing. The device will provide a fake network running fake email and web servers and using some network trickery, will capture the hostname, username and password of any attempted connection and log it, along with the GPS co-ordinates of where the details were captured. This device could be used to hijack corporate and personal email logins, facebook logins, and so on.
Messing around with airbase-ng, part of the aircrack-ng suite over the last few months and researching wireless client vulnerabilities has led to an interesting proof of concept project. There are several weaknesses within the current wireless technologies in widespread use. First however, an explanation of the project. The project description was to launch a wireless man in the middle (MITM) attack, without having another end to connect the victim to. We need to create a MITM attack without having any internet access. Such an attack could theoretically be used on the tube, in locked down buildings, on the move, and so on, and without the use of a mobile data card. Built on top of a modified raspberry pwn release, although any Linux distribution would have been suitable, I have set my wireless device with a power output of 30dBm and started the following automated process:
Firstly, an airbase instance on my rtl8187 card as follows;
/usr/local/sbin/airbase-ng -c 3 wlan0 –essids “/root/pen/code/scripts/essids” -P -C 60 -I 60 -vv|grep –line-buffered “directed probe request”|tee /run/probes
This starts an access point on channel 3, beaconing the SSIDs contained within /root/pen/code/scripts/essids as well as any probe requests that the access point may receive from clients looking to connect to an access point. Now, in a little more detail, regular ‘non-hidden’ access points will broadcast ‘beacons’ which are pieces of data that specify the SSID (wireless network name) as well as the supported encryption types and so on. These beacons are usually sent every 100msec. Wireless clients will send probe packets, containing the SSIDs of all wireless networks that they have stored, and asking if any of them are here.
The -P switch to airbase-ng will have airbase respond to all probes saying “yes, that’s me” at which point assuming the encryption or lack thereof matches the stored profile, the client will attempt to associate. Mid way through building this test however, Apple released IOS 6, and one of the changes seems that the iPhone will now only send out broadcast probes rather than directed probes, rendering the -P feature useless against them. The broadcast probe is where the device sends out a “is anyone there?” probe, and waits to see which access points reply. Most iPhones however have connected at some point to a wireless hotspot, and so the SSIDs I chose for the essids file are “Boingo Hotspot”, “BTOpenzone” and “BTWiFi” in the UK. I believe that “attwifi” is a popular one in the US.
We then wait for airbase-ng’s `at0′ interface to come up, before starting a DHCP server handing IPs out on the 10.0.0.0/16 range whilst at0 itself is set to 10.0.0.1. Clients are set with DNS and router set to 10.0.0.1.
We then create a DNAT entry with iptables to redirect any traffic that comes in on at0 that would have been routed back to ourselves on 10.0.0.1;
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -i at0 -j DNAT –to-destination 10.0.0.1
Remembering that we have no default gateway, the biggest issue we have is that whilst we can run fake services on our device, we have no way of performing DNS lookups, and therefore even if we respond to all DNS A requests with ‘10.0.0.1’, we’ll most likely be logging useless credentials.
At this point, I thought it would be a good idea to brush up on my programming skills and relearn PERL. Using the POE framework and sqlite3, we next run a fake DNS server. The DNS server is assigned a range, in this case 199.0.0.0/8 on which to hand out IPs. The first request is assigned 199.0.0.1 and logged in the database, the second request 199.0.0.2, and so on. If we already have a record of that request, we’ll hand out the IP we handed out the last time. Whether the client accepts our DNS or has their own hardcoded, the DNAT will redirect any DNS request to our device. Our DNS table might look something like;
| id | ip | host |
| 1 | 199.0.0.1 | apple.com |
| 2 | 199.0.0.2 | www.google.com |
| 3 | 199.0.0.3 | m.google.com |
| 4 | 199.0.0.4 | imap.gmail.com |
Now, iDevices and Blackberries attempt to connect to a URL to confirm internet service. If they do not receive the expected response, they assume they are on a wireless hotspot and pull up a login page. We must satisfy the query to pretend to the devices that they have valid internet access.
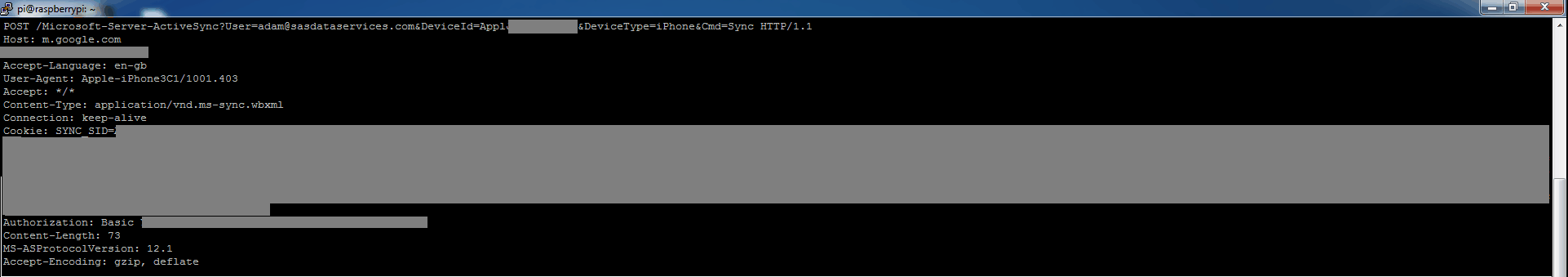
The next step in the process is where the client tries to connect to a service. I have currently built protocol support for POP3, IMAP, HTTP and their SSL versions, and additional services can be added easily.
Once the client initiates a connection, it is redirected back to us over DNAT. Under Linux, we have the originally requested destination IP available by using the socket option SO_ORIGINAL_DST. Assuming the client attempts to connect to 199.0.0.3 now over IMAP, our IMAP server implements enough of the protocol to log the credentials and keep the client happy, as well as looking up the requested hostname ‘m.google.com’ in the sqlite3 database and presenting it as the banner.
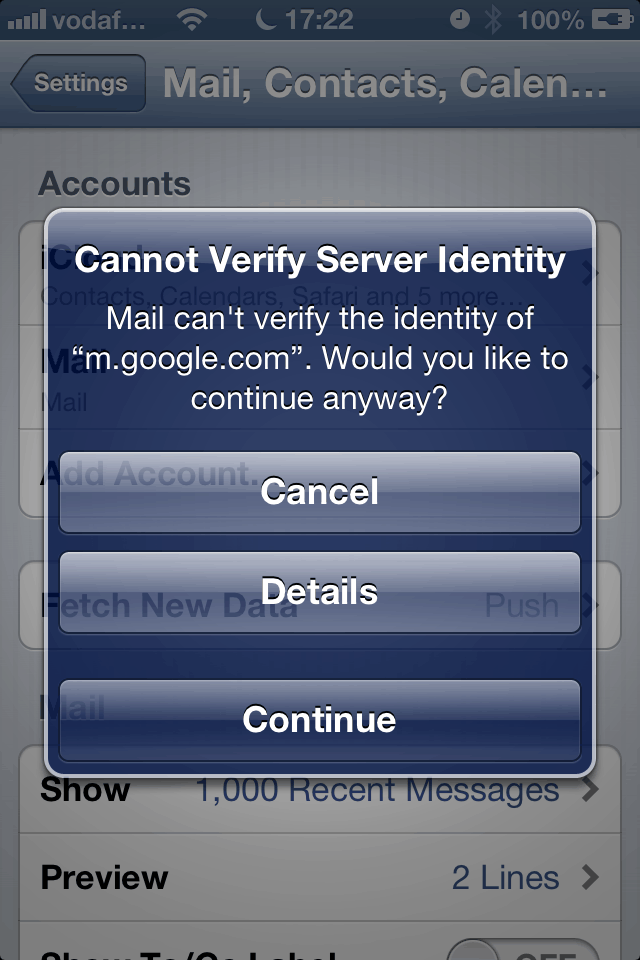
Should SSL be in use, we dynamically create a self signed certificate for ‘m.google.com’ and present it to the client. It will yield the usual SSL warning although having a matching hostname, the non-technical user is more likely to accept. The iPhone [4 at least] had an annoying feature where no matter how many times ‘cancel’ is clicked, it will keep presenting with the same SSL warning until ‘continue’ is clicked or wifi is shut off. This almost guarantees that the user will click continue. In addition, whilst testing, I did not even realise at first that the warning I was presented with on the iPhone was even an SSL certificate warning. I am very surprised that the warning is not worded in stronger terms than it is.
Once we have credentials, these are logged in a separate table and related back to an IP entry which ultimately relates back to the original host the user attempted to connect to. Thus we are able to log host details, username and passwords on a standalone portable device with no network connectivity. Lastly, the device was kitted out with a BlueNEXT GPS dongle, and so GPS coordinates can be logged if they are available for where credentials were sniffed.

It is not legally possible to actively run such a device in public, however based on internally testing the system with my own devices, as well as passively collecting some of the broadcast probes sent over the air in public places, running such a device in public could very easily harvest many hundreds of passwords ranging from home to corporate in only a few minutes at a suitably busy location. Furthermore, as the device has no internet or external connectivity of its own, and the attacker would be entirely untraceable.
In my next posting, I will discuss some of the weaknesses we touched upon and how they can be overcome.
source: http://www.iodigitalsec.com/fully-automatic-wireless-hacking-station/
相关内容:
全自动无线入侵热点,黑客全自动WIFI钓鱼,大规模批量无线热点钓鱼
WiFi流量劫持:网站JS脚本缓存投毒!长期控制!浏览任意页面即可中毒!
如何入侵控制交通红绿灯?美研究人员发现劫持交通灯其实非常简单
某款网络摄像机直接获取帐号密码,视频监控设备配置信息泄露漏洞
讨论电影中出现的各种骇客、黑客入侵手法,《幽灵》、《神探夏洛克》
使用WiFi真的有那么危险吗?安全科普:教你增强自己的无线网络安全
WiFi里的猫腻:变色龙病毒,无线破解、蹭网,蜜罐路由器,黑吃黑
黑客讲故事:攻下隔壁女生路由器后,我都做了些什么,无线路由器被蹭网后,入侵女神
女黑客Oona,分析直升机现场拍摄警车追捕画面中的信号声,绘出飞机飞行轨迹
指纹门控的安全,户外物理设备入侵,如何入侵绕过指纹识别安全锁、门控系统
揭露一个飞机退改签的诈骗:借口机票退改签要退款,索要银行卡号,套取个人信息
已更新Iwork10测评!求推荐一款便携式户外物理移动渗透终端设备!!!
一基友再遇奇葩无线网络环境,顺便求二级/三级/四级ISP的盈利方式?
Hikvision IP Cameras Multiple Vulnerabilities,海康威视IP摄像机的多个漏洞
Hikvision IP Cameras Multiple Vulnerabilities, 海康威视IP摄像机的多个漏洞
已获得网络出口引擎管理员权限,试问监控全网HTTP密码传输可能性?
浅谈社工,欢迎讨论、补充,各种猥琐社工、人肉技巧,物理社工、人肉
【TED】Markham Nolan:如何辨别网上信息真伪,神级人肉,物理社工
ATM 机里装着什么?ATM 机的结构是什么?ATM 的构造原理?
关于伪基站的一些问题:信号覆盖范围?设备成本?是否违法?教程资料?
伪基站是怎么定位的呢?定位并抓捕伪基站、圈地短信、垃圾短信犯罪团伙!
讨论:通过无线路由渗透入侵内网电脑,如何从无线路由器到个人PC机?
谈谈时事:电话“诈”弹导致多地机场飞机被迫返航,论如何打电话不被追踪
小米云服务同步“wlan设置”的安全性,小米已收集了32万wifi明文密码
(视频)USRP 来Sniffing 无线键盘,27Mhz keyboard sniffing
(视频)USRP 来 Sniffing 无线键盘,27Mhz keyboard sniffing
(视频)USRP 来 Sniffing 无线键盘,27Mhz keyboard sniffing
全面披露华硕十款无线路由器 - AiCloud启用单位的多个漏洞
超级短信DDOS 女生一天收上万条10086短信 还有近50万条等着她
讨论如何通过航空飞机的互联网入侵、劫持飞机上的乘客,入侵劫持卫星
R820T电视棒+软件无线电跟踪飞机飞行轨迹(SDR&ADS-B)
rtl-sdr,RTL2832+E4k tuner电视棒跟踪飞机轨迹ADS-B/TCAS/SSR
rtl-sdr,RTL2832+E4k tuner电视棒跟踪飞机轨迹 ADS-B/TCAS/SSR
电视棒跟踪飞机轨迹教程(ADS-B), SDR GPS 飞机追踪
rtl-sdr,RTL2832电视棒跟踪飞机轨迹教程(ADS-B), SDR GPS 飞机追踪
视频: Dtac:将宠物变成了WiFi热点,泰国运营商将宠物变成WiFi热点
户外物理设备入侵之:入侵并“调教”中控指纹语音考勤系统(打卡机)
GNU Radio USRP OpenBTS 小区短信 区域短信
一种牛逼的短信群发技术 GNU Radio 小区短信 区域短信 免费发 无法拦截
周末湖边 Sniffing ADS-B,Hack 私人小型机场
视频: ATM 的那点事! ATM 漏洞, Hack for fun! 利用磁卡导致ATM关机
Inception能入侵全盘加密的计算机,修改物理机器内存/任意密码进入
android软件外加监控,隐私安全?!爆个一键root内幕!
关于X卧底的通话监听、短信记录、定位追踪等侵犯隐私的行为讨论
远程入侵QQ好友所在网吧监控系统,人脸识别、定位坐标,定点打击
dSploit—Android网络渗透套件测试小记(含视频)
实时抓取移动设备上的通信包(ADVsock2pipe+Wireshark+nc+tcpdump)
武汉公安开发尖端人像识别系统 可瞬间辨认嫌疑人 全国摄像头寻人
美国极超音速飞机90分钟飞越半球,时速可达4000千米,飞行在太空边缘
单反刷成安卓/ios,手机 psp kindle,连文曲星 计算器 空调遥控器也不放过
视频:FPSRussia的俄式军火秀 遥控武装四桨直升机[中英双语字幕]
免费 WiFi 是“披着羊皮的狼”,女子蹭网引来20多名警察
Flightradar24 网站“直播”天上“堵飞机” 看全球实时航班
用音响打电话,揭秘柯南电话拨号,如果电话键失灵了,直接用音响打电话
用音响打电话,揭秘柯南电话拨号,如果电话键失灵了,直接用音响打电话
iPhone 短信欺骗漏洞攻击器、伪造短信号码工具、伪装发件人攻击器
Never trust SMS: iOS text spoofing,永远不要相信短信:iOS的文字欺骗
iPhone 短信欺骗漏洞披露,伪造短信号码、自定义短信手机号
德安全专家破解GSM加密算法 GSM网络破解 监听全球40亿部手机
拉斯维加斯国际黑客大会(DefCon 2012黑客会议)本周开战
802.11b 无线网络固件级攻击、802.11b Firmware-Level Attacks
手机全息投影、初音、Miku、立体投影,制作方法已放出,图文+视频
从技术角度深入剖析:改号软件,电话号码任意显示,伪造来电显示
华裔黑客 BITcrash44 凭借一台 iPhone4 拿下时代广场大屏幕
视频:国外黑客利用一部诺基亚N95手机入侵火车站电子屏,并且现场直播
视频:漂浮在空中的水珠、静止的水滴,适合做成展品的视错觉,超炫!!
利用电磁波进行入侵、原子级的黑客入侵、利用电磁波毁坏物理设备
电视机会收到邻居游戏机画面?小霸王信号干扰?红白机功率这么强悍?
视频:鬼佬的室内四轴定位系统,震惊,飞机模型能玩到如此地步!
ATM Skimmers - ATM Hacker - 自动提款机黑客
用黑客方式找回失窃的电脑 - GSM基站定位 - Wifi热点定位
不要偷黑客的东西 - Why you don't steal from a hacker
【视频】发射到121000英尺(36880.8米)摄影机拍摄地球
美国“末日飞机”曝光 面临大灾难可保护首脑 可抗核武器袭击、核辐射
视频:黑客实战入侵,黑客入侵大楼灯光控制系统,黑客们的游戏,户外物理入侵
留言评论(旧系统):